This is an AI for Health MSc project. Students are elgible to receive a monthly reimbursement of €500,- for a period of six months. For more information please read the requirements.
Clinical Problem
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) has the worst prognosis of all cancer diseases with a 5-year survival rate of less than 10%. Early detection can help improve outcomes but is challenging due to the absence of specific clinical symptoms in the initial disease stages and the current lack of tools for early tumor detection. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging has the ability to assist in the identification of early tumors, which are often small and iso-attenuating on routine computed tomography scans, by providing better soft-tissue resolution. Nevertheless, a large number of patients are still misdiagnosed by radiologists based on imaging, leading to inaccurate treatment indications and prognostication. Deep learning has shown great potential to facilitate and improve clinical decision-making by considering large amounts of imaging data, but its application for PDAC diagnosis on MRI images is currently unexplored.
Solution
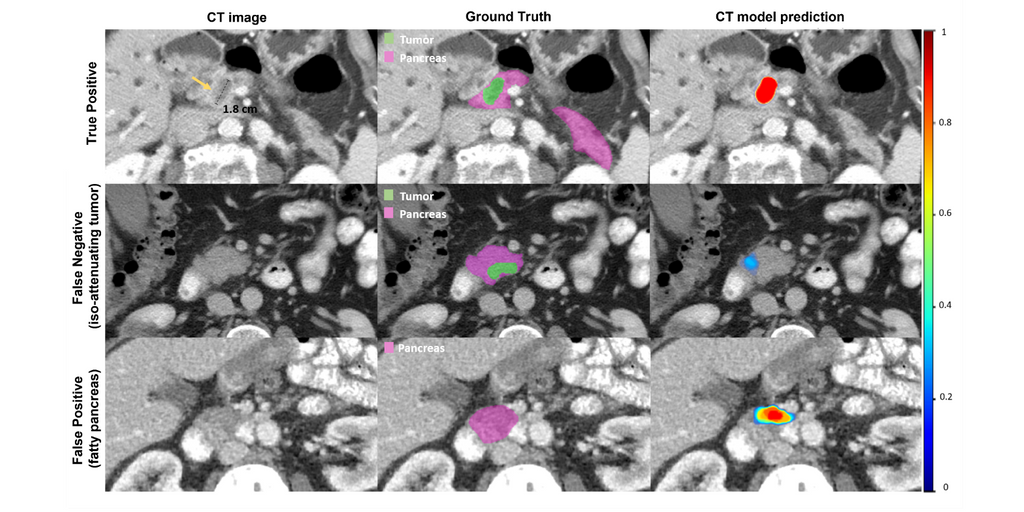
The goal of this project is to explore deep learning for the automatic detection of PDAC in MR images, with a focus on small, early-stage lesions. The challenge is to leverage large amounts of MR data, in a semi-supervised approach using self-learning. In our team we already developed a framework for tumor detection on CT images and we want to see how the MR approach compares, specially in cases where the CT model fails such as for fatty pancreas and iso-attenuating tumors (see image).

Results
The algorithm will be made available as a Docker container on https://grand-challenge.org/. It can then be applied to MR scans from hospitals that use the grand-challenge infrastructure.
Data
Radboud UMC archive currently contains more than 1000 pancreatic MR images, including normal and tumor cases, which can be used for training/testing the models. This project will use annotated data from an ongoing prospective study containing about 100 pancreatic cancer patients.
Embedding
This work will be integrated into PANCAIM, a European consortium project with the aim of using AI to generate breakthrough knowledge in pancreatic cancer care. The project promotes collaboration with several institutions ranging from clinical/academic partners, which contribute with external data for model testing, to industrial partners such as Siemens Healthineers, which will promote the rapid implementation and validation of the generated models in clinical practice.
Requirements
- Students Artificial Intelligence, Data Science, Computer Science, Bioinformatics in the final stages of their Master education.
- You should be proficient in python programming and have a theoretical understanding of deep learning architectures.
- Basic biological / biomedical knowledge is preferred.
Information
- Project duration: 6 months
- Location: Radboud University Medical Center
- More information can be obtained from Natalia Alves (mailto: natalia.alves@radboudumc.nl)
